Bioelectronic assays monitor in vitro cell health and behavior.
Without labels, bioelectronic assays capture real-time data for minutes or days in a single plate. Sensitive electrodes in the plate track small cellular changes, revealing information often below the detection limit of other techniques.
There are many kinds of assays to quantify cellular activity in vitro but bioelectronic assays are ideal for high-throughput live-cell monitoring.
Have questions about how to use bioelectronic assays in your studies
What is a bioelectronic assay?
Types of bioelectronic assays
Extracellular electrophysiology recordings with MEA bioelectronic assays
Live cell analysis with impedance-based bioelectronic assays
Cell barrier integrity measurements with TEER assays
Bioelectronic assay platforms
Frequently asked questions about bioelectronic assays
What is a bioelectronic assay?
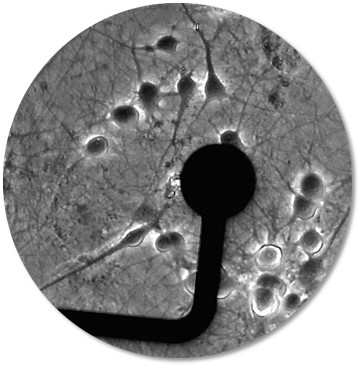
A bioelectronic assay uses biocompatible electronic microsensors to continuously monitor living cells, detecting cell number, morphology, signaling, and even electrophysiological activity without additional labels or dyes.
Cells are cultured on electrodes embedded in the bottom of microtiter plates. Measurements do not alter the cell’s biology and may be collected for prolonged times. With this continuous data you will never miss a data point.
Bioelectronic assays provide more information with less work creating a direct interface between biology and electronics for the rapid development of new drug candidates in healthcare and medicine.
Types of bioelectronic assays
The three major types of bioelectronic assays are:
- Microelectrode array or multielectrode array (MEA) electrophysiology assays measure the electrophysiology of electrically active cells such as neurons and cardiomyocytes.
- Impedance-based cellular assays monitor the presence, morphology, and behavior of any cell type in culture.
- Transepithelial or transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) assays are based off impedance technology. These assays quantify cell barrier integrity.
Extracellular electrophysiology recordings with MEA bioelectronic assays
Multi-electrode array (MEA) systems are readily used for electrophysiological studies to understand electrically active cells such as neural networks and cardiac syncytia.
Multielectrode arrays captures the field potential or activity across an entire population of cells, with far greater data points per well, detecting activity patterns that would otherwise elude traditional assays such as patch clamp electrophysiology which probes a single cell such as a neuron.
MEA systems are the perfect solution to high-throughput in vitro electrophysiology.
Applications include, but are not limited to:
- Cardio- and neurotoxicity evaluations
- Cardiomyocyte classification and development
- Cardiomyocyte Inotropy
- Neural organoids
- Neural co-culture populations i.e. neurons and glia cells
- Neurological and neurodegenerative diseases i.e. ALS, autism, epilepsy
- Neuromuscular junctions
- Zebrafish
Live cell analysis with impedance-based bioelectronic assays
Impedance-based or live-cell analysis assays are sensitive to many aspects of cell behavior: attachment, morphology, cell-cell interactions (e.g. tight junctions), and number. Even small transient changes, such as swelling or signaling, are detectable by impedance. Because impedance is noninvasive and label free, the dynamics of these changes can be monitored in real time over minutes, hours, or even days without disturbing the biology.
Immune cell-mediated killing of cancer cells uses the body’s own immune cells to target and destroy tumors. Evaluating the potency of these therapies in vitro, before they reach the patient, remains a challenge.
Simple and sensitive, Axion BioSystems' bioelectronic assays collect continuous data, revealing the full response and kinetic interactions of immune cells and cancer label-free and in real-time.
Applications include, but are not limited to:
- Cytotoxicity and cell viability
- Immuno-oncology
Cell barrier integrity measurements with TEER assays
TEER (transepithelial or transendothelial electrical resistance) assay is based off impedance technology. A small AC current is passed from one electrode to another. TEER measures how much of this electrical signal is blocked by the cellular layer, thereby quantifying barrier integrity.
Because impedance is non-invasive and label-free, the barrier can be continuously monitored for minutes, hours, or even days without disturbing the cellular biology
Applications include, but are not limited to:
- Barrier function/TEER
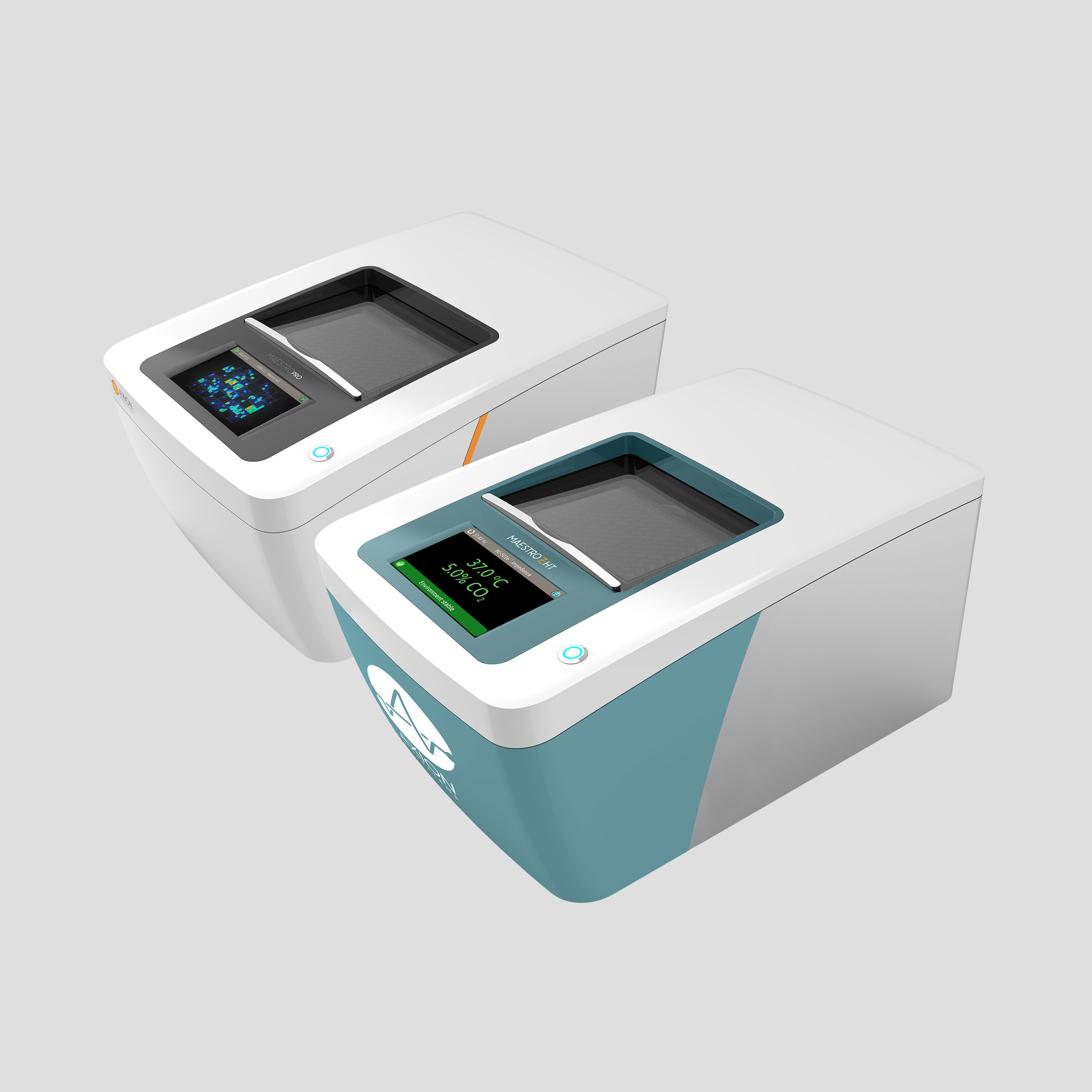
Bioelectronic assay platforms
Axion offers four bioelectronic assay systems: Maestro Pro, Edge, Z and ZHT as well as a selection of multiwell plates and custom software modules.
Bioelectronic Assay Systems
Impedance systems – deliver high-quality impedance results with a thin, transparent bottom for culture visualization. Available in 96- and 384-well plate formats.
MEA systems – provides high-quality MEA results together with industry-leading throughput. Available in 6-, 24-, 48-, and 96-well formats.

Assay Plates
Impedance multiwell plates – deliver high-quality impedance results with a thin, transparent bottom for culture visualization. Available in 96- and 384-well plate formats.
MEA multiwell plates – provides high-quality MEA results together with industry-leading throughput. Available in 24-, 48-, and 96-well formats.
Software
Our suite of platforms are available with five software modules: Neural, Cardiac, MEA Automation, Impedance and GxP Impedance. Select the software modules to match your assay needs:
Neural – Measure the key parameters of neural network function, including activity (are the neurons functional?), synchrony (are the synapses functional?), and oscillation (is the network functional?).
Cardiac – Record the four key measures of functional cardiac performance, label free and in real time in every well of the multiwell plate: action potential (a.k.a. LEAP assay); field potential; propagation; and contractility.
MEA Automation – Automate Cardiac and Neural MEA assays with this API for interfacing with liquid handling platforms.
Impedance – Track cell proliferation, morphology, and viability label-free and in real-time. Ideal for immuno-oncology, cytotoxicity, virology, cell migration, cell proliferation, GPCR assays, and many more.
GxP Impedance – Achieve FDA 21 CFR Part 11 compliance in GMP/GLP labs with this version of the Impedance Software Module.
Help me select the system that is right for my studies
Frequently asked questions about bioelectronic assays
What is the difference between bioelectronic assays and bioelectronic medicine?
Bioelectronic assays non-invasively monitor the health and activity of your cells in vitro. This benchtop technology is well suited to multiple disease models and therapeutic development.
Bioelectronic medicine is a new approach to treating and diagnosing injury and disease in a patient, in vivo, often focused on electrical signaling in the nervous system.
What are the benefits of using Axion BioSystems' bioelectronic assays in my research?
- Easy to use high-throughput, in vitro systems with full environmental control.
- Non-invasive, label-free recording from cells or organoids.
- Simple work flows require only basic cell culture techniques.
- Continuous recording captures complex culture dynamics in a single plate in acute or chronic experiments
- User-friendly software for acquisition and analysis.
