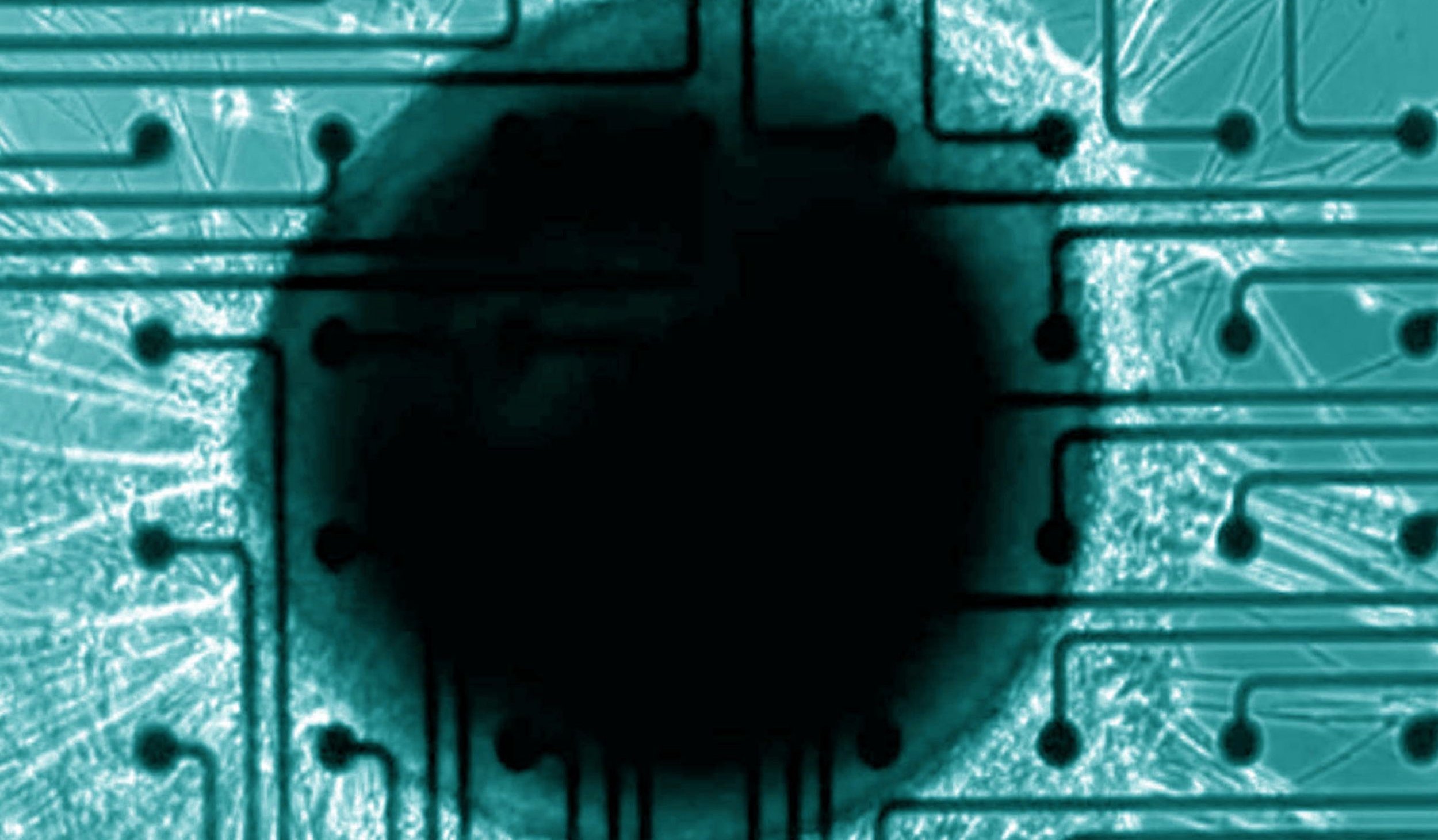
Neural organoids and spheroids are three-dimensional in vitro cell cultures that recapitulate aspects of human brain physiology, structure, and developmental processes. With whole-brain and region-specific phenotypes like cortical, cerebral, or spinal organoids, neural organoids have become popular for investigating neural development, disease progression, and drug safety—helping to bridge the gap between animal models and clinical research.
The Complete Workflow for Neural Organoid Assays
Combine platforms to study your organoids from start to finish
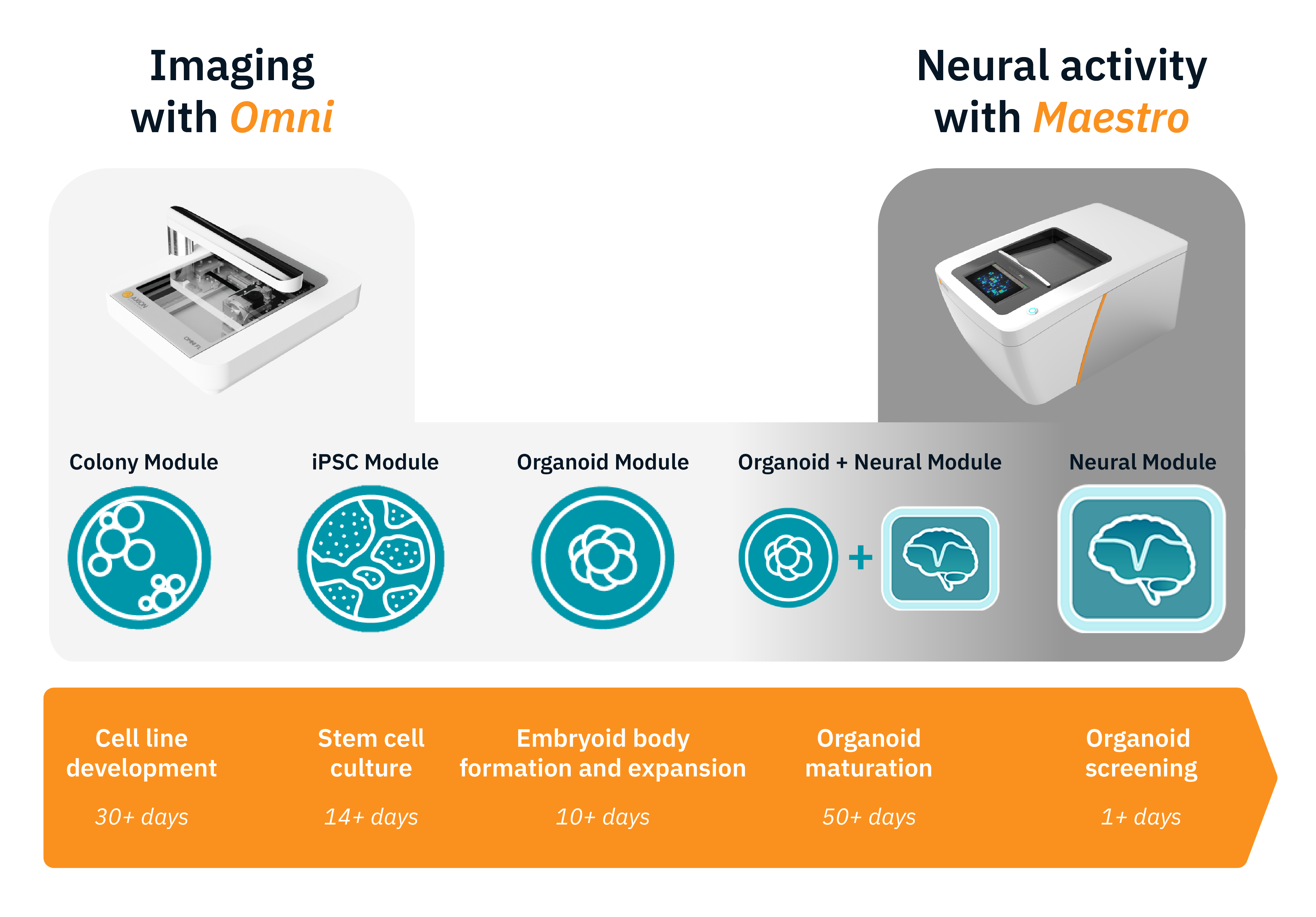
Better data starts with consistent organoids. Monitor your stem cell cultures and organoid formation on the Omni before you assay, then track neural network development and maturation with the Maestro MEA.
Omni live-cell imaging platform
- Monitor stem cell cultures
- Track organoid formation and growth
Maestro MEA platform
- Record neural activity
- Measure network and LFP development
Functional Analysis of Neural Organoids
-
Standardizing organoid production and analysis>
-
Measure neural spiking and local field potentials simultaneously >
-
Study the development and maturation of brain networks >
-
Develop models of neuroimmune organoid network development>
-
Neanderthal mini-brains>
-
Recording functional activity from cerebral organoids>
-
Assay Steps: Plating neural organoids for measuring activity >
Quality neural organoid research requires the right tools from start to finish.
Watch this 8 minute video to discover how Axion's imaging and MEA platforms allow you to capture the complex biology of organoids non-invasively and in real time.
Purpose: To simultaneously measure neural spikes and local field potentials (LFPs) in neural organoids. Organoids can recapitulate aspects of the complex structure and networking of the brain, developing LFPs detectable beyond the surface firing.

Neural organoids were recorded on the Maestro MEA platform. The MEA Viability module was used to verify organoid placement and attachment.
Result: Neural spikes were only detected on the periphery. LFPs were recorded from the interior of the organoid, in regions where surface spiking wasn’t detected.
Purpose: To model human brain development with cortical organoids. Altered brain development in utero can have lifelong consequences but a lack of appropriate in vitro models limits our ability to investigate these processes.
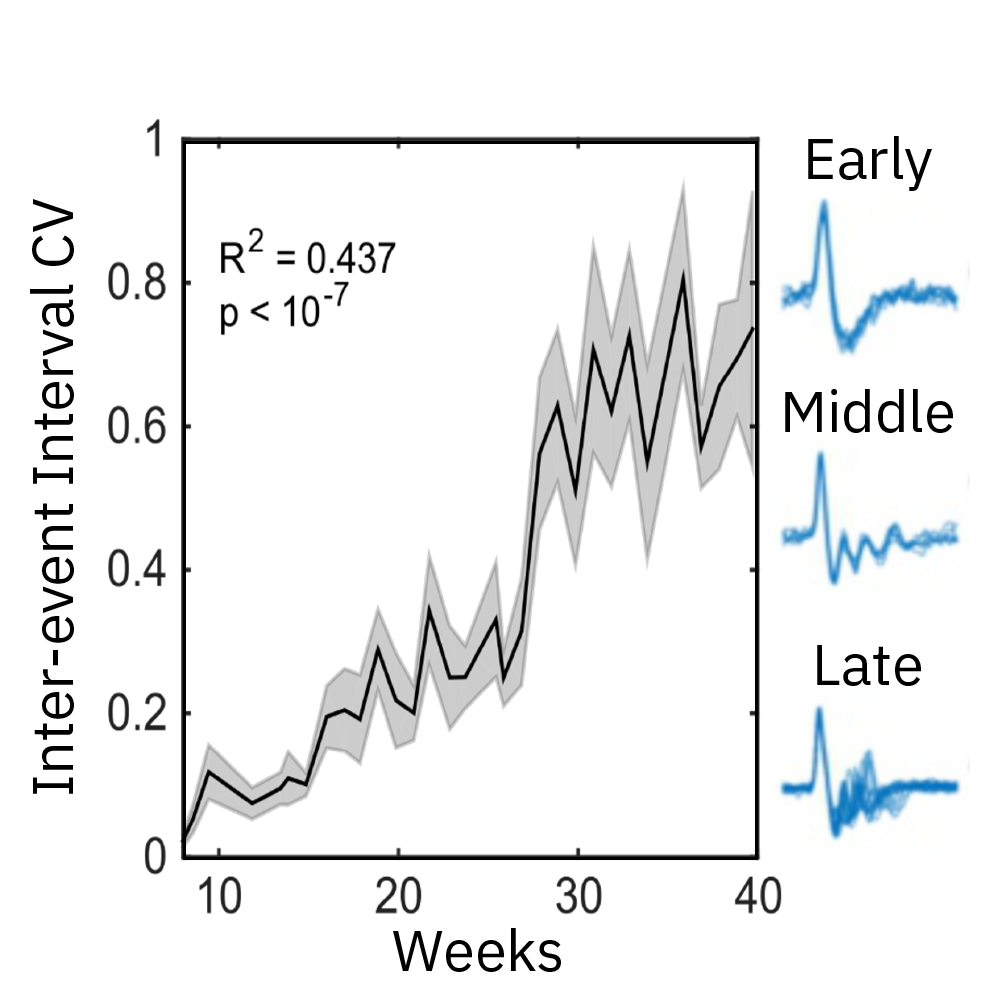
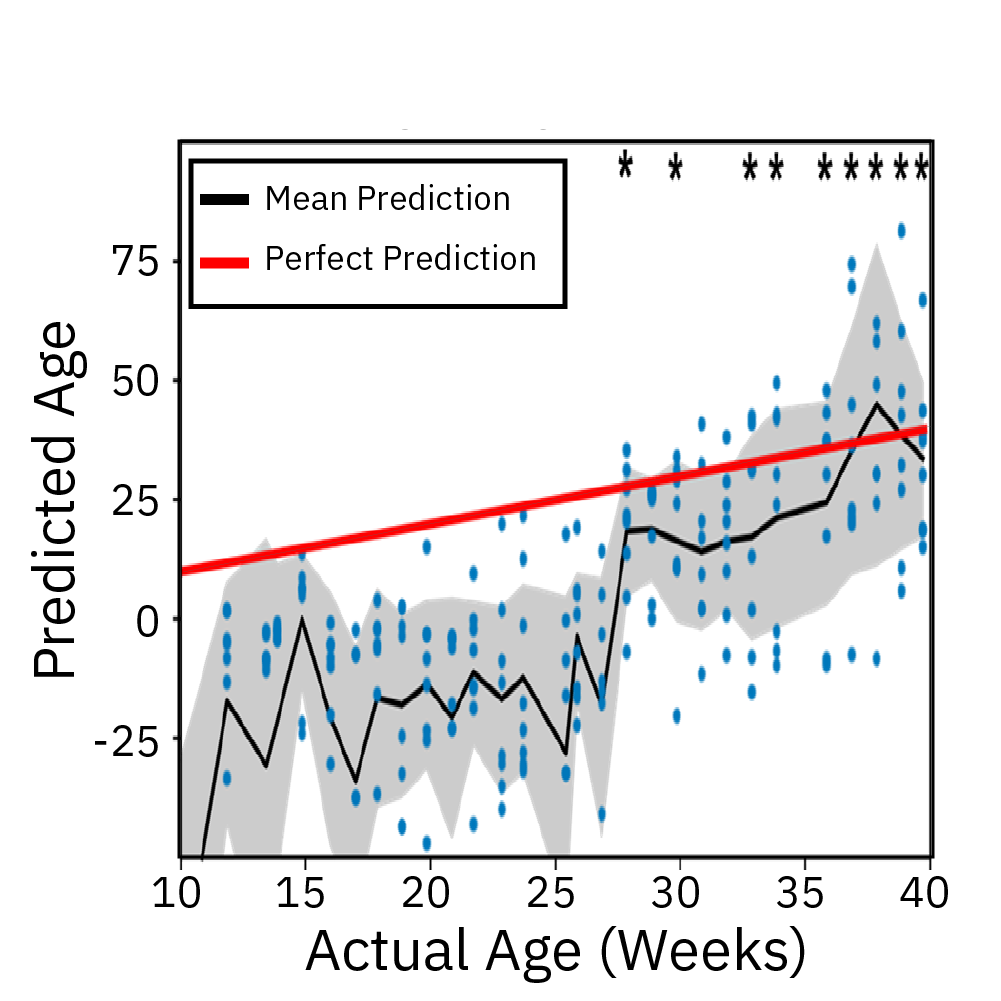
Extracellular recordings of spontaneous electrical activity of neural organoids were measured using the Maestro MEA platform over the course of 10 months and compared to neonatal EEGs.
Result: Cortical organoid activity demonstrated a continuously evolving neural network growing in complexity from early, middle and late time points. Organoid maturation and development were found to mimic the development of the preterm neonatal brain. Watch this webinar to learn more.
Three-dimensional neural organoid models provide a promising platform for investigating the impact of glial cells on neural activity and exploring their complex role in the pathogenesis and progression of neurological and neuropsychiatric disease. In Popova et al, Cell Stem Cell 2021, the authors compared human microglia across culture models and used the Maestro Pro MEA platform to demonstrate how transplanted microglia accelerated the emergence of synchronous, oscillatory network activity in cortical organoids in vitro.
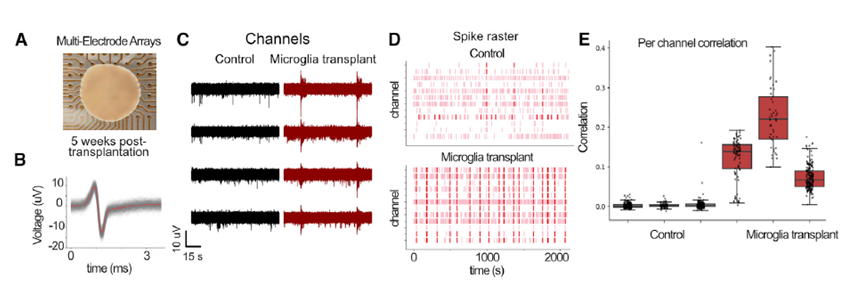
Cortical organoids on multiwell Maestro MEA system
The genomes of Neanderthals and modern humans are very similar. By investigating the differences in genetic make-up, we can gain insights into what separated modern humans from our extinct relatives. In this webinar, Cleber Trujillo, PhD (StemoniX) discusses how he introduced an archaic variant gene, NOVA1, into human pluripotent stem cell-derived brain organoids and evaluated the impact on neural activity as recorded on the Maestro MEA system.
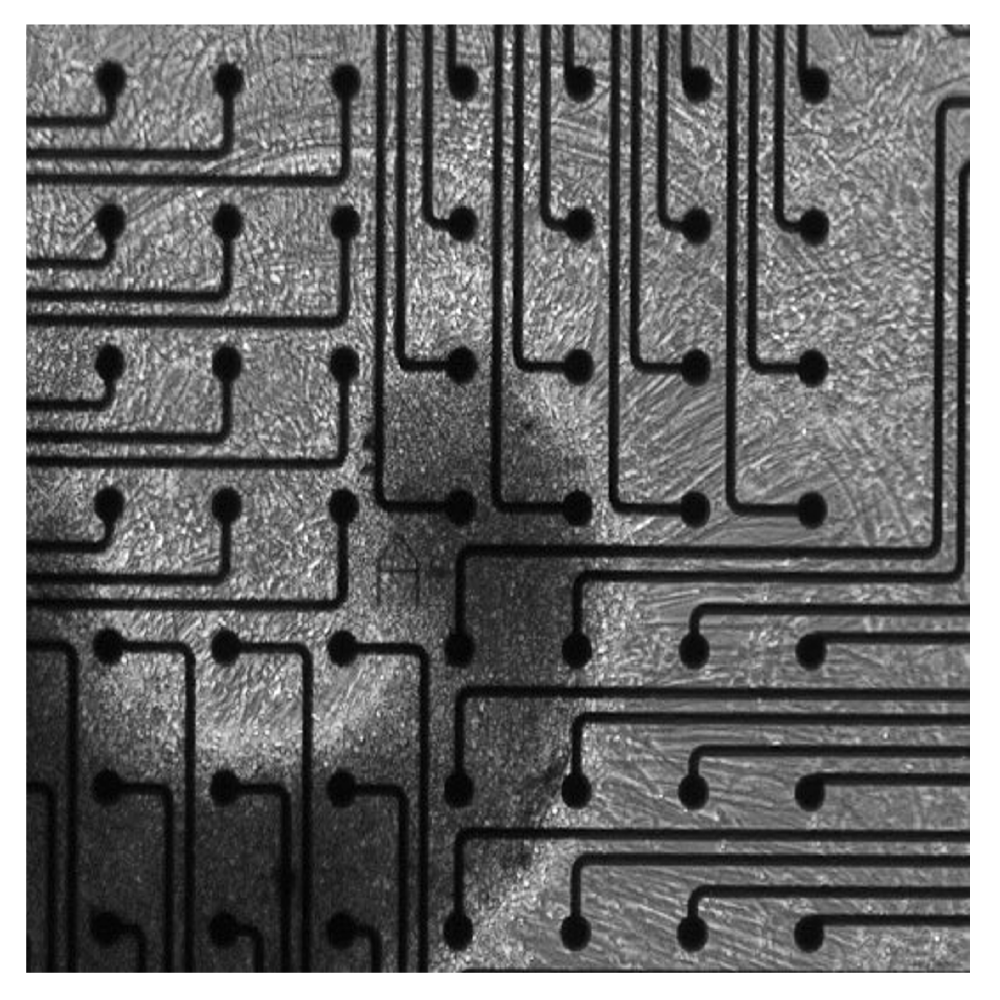
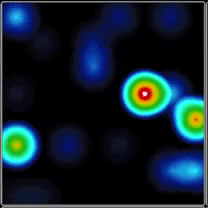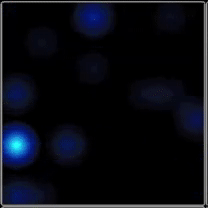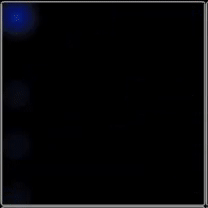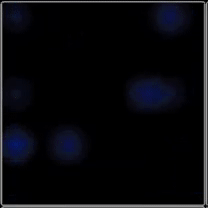
Electrical activity is measured from organoids cultured on electrodes. Cerebral organoids generated from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) exhibit spontaneous neural activity, with increasing complexity as networks mature. Since the microelectrode array is two dimensional, signals recorded reflect the activity of the neurons on the bottom of the organoid. For the best results, ensure contact between the electrodes and the bottom of the organoid.
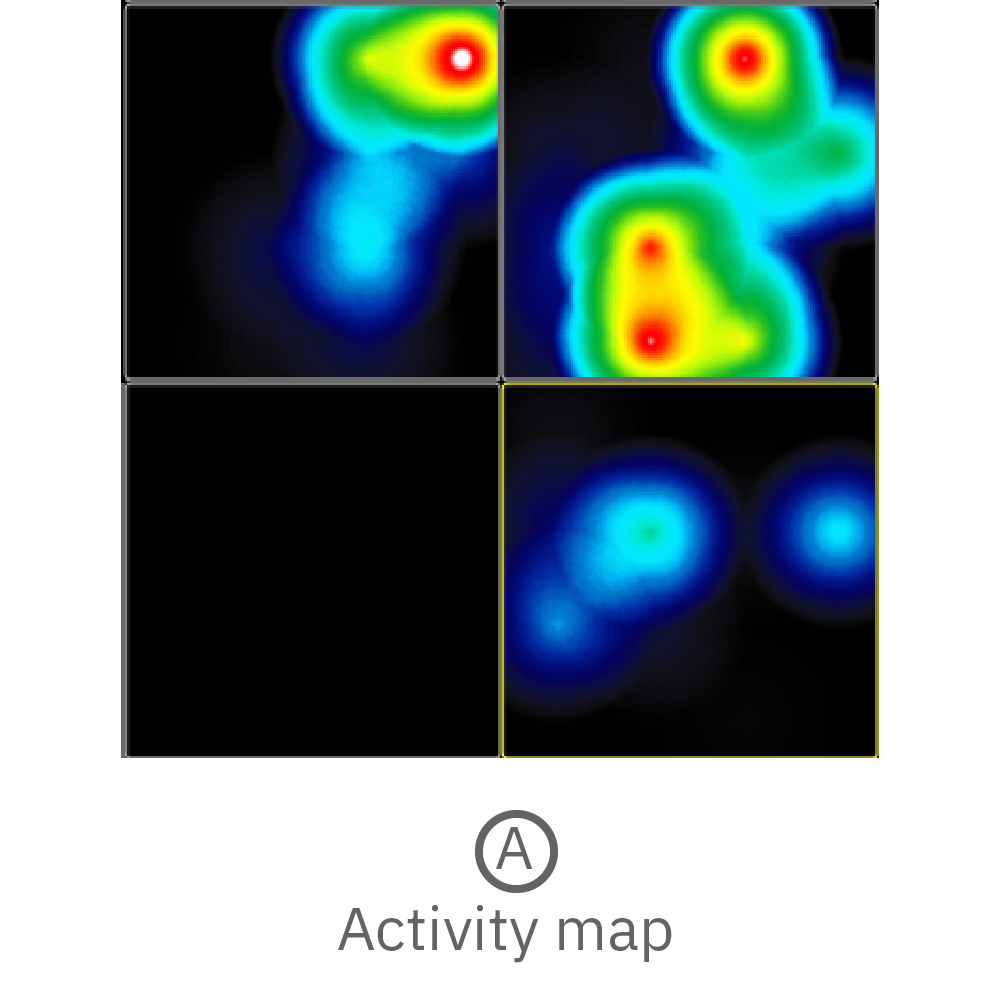
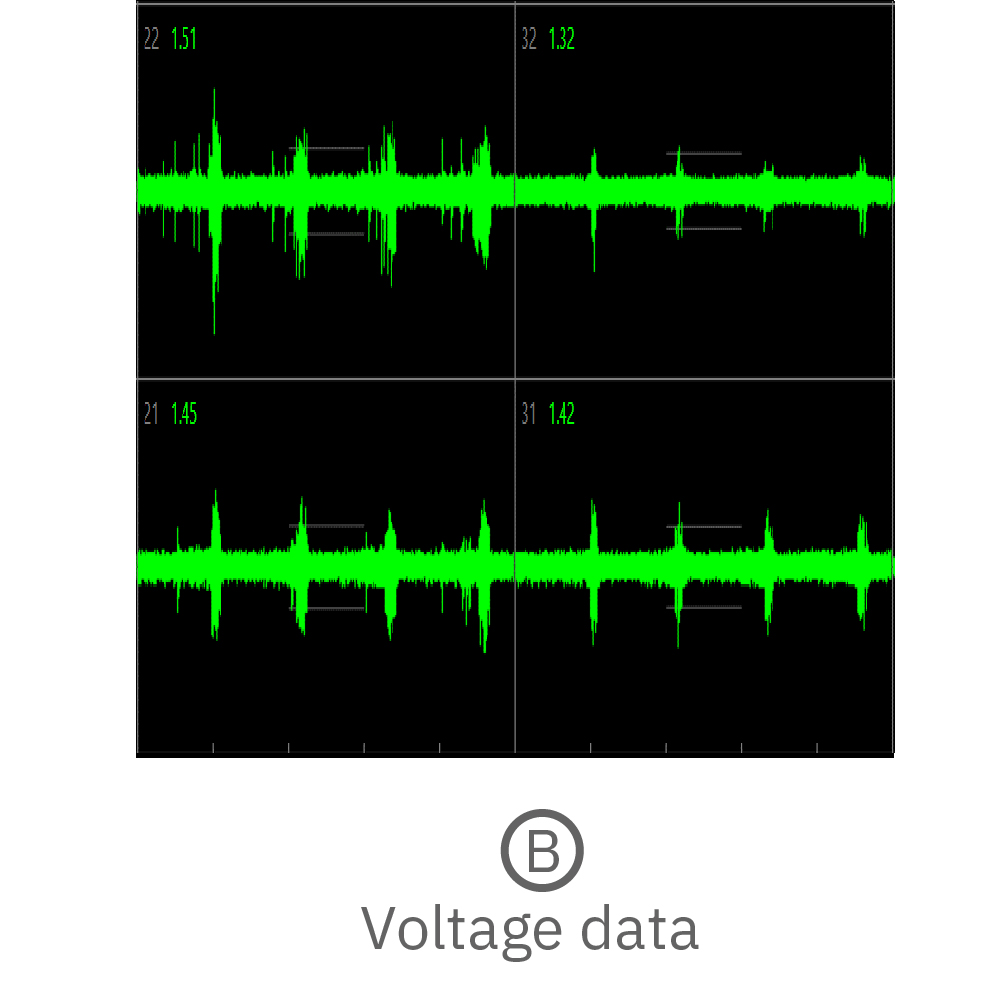
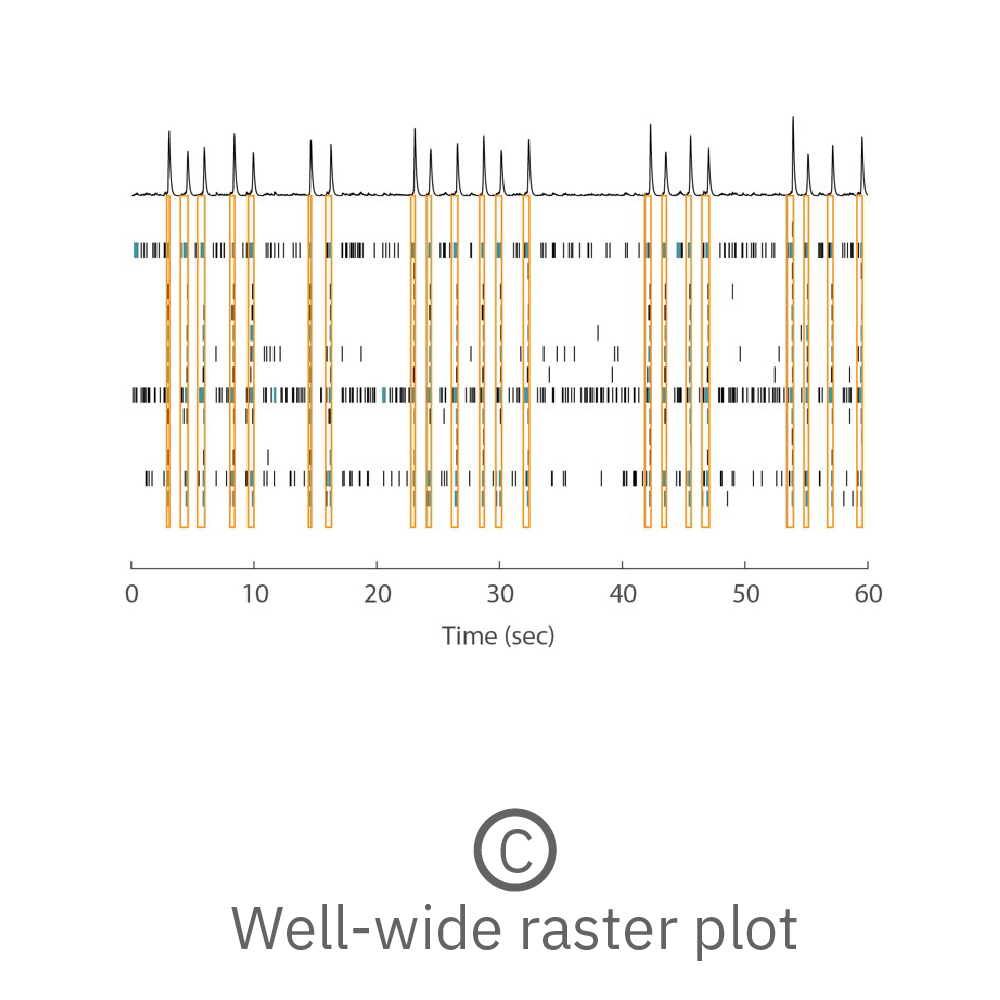
(A) Activity map displaying instantaneous firing rate of four wells with multiple cerebral organoids in each well. (B) Continuous voltage data recorded from four electrodes in one well. Activity is recorded from different sites on the same organoid. (C) Well-wide raster plot showing activity across all 16 electrodes and synchronous network bursting. Teal tick marks indicate electrode bursts, and orange boxes indicate network bursts. Data provided by Maestro customer.
Whole neural organoid plating for MEA recording
This protocol describes a method for plating whole neural organoids on an MEA for measurement of spike and LFP activity.
Plating of sliced neural organoids for MEA recording
This protocol describes a method for creating organoid slices for plating on an MEA for measurement of spike and LFP activity.
The MEA System for your Neural Organoid Assays
From characterizing the development of disease to discovering tomorrow's therapeutics, the Maestro MEA platform offers unparalleled insights to transform your organoid research. Its versatility and ease-of-use combined with high content, functional activity profiling make it a robust translational tool for any lab.
Neural Organoid Publications and Resources
Neural organoids are rapidly changing the field of neuroscience. See how researchers are using Axion’s live-cell analysis tools to accelerate their organoid research with publications, webinars, application notes, and more.