抗ウィルス薬の開発は、ウィルス研究の重要な焦点の1つです。しかしながら、体内の機能に悪影響を及ぼさず、ウィルスのみを抑制する抗ウィルス薬の開発は、容易ではありません。一方で、ウィルスは急速に変異し、それに伴い新たな抗ウィルスのターゲットが生まれ、従来の薬剤の抗力が低下します。近年の SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)、エボラ、ジカ、インフルエンザなどのウィルス感染症の流行により、広範囲のウィルス感染に有効な抗ウィルス薬の開発に力が注がれています。
Axion BioSystems の Maestro システムは、インピーダンスの変化により、細胞の状態をリアルタイムで分析します。ウィルス感染による細胞変性効果 (CPEs)を、ラベルフリーで観察することが可能です。細胞の状態を経時的にトラッキングすることにより、抗ウィルス薬開発に有用な多くの情報を得ることができます。
抗 SARS-CoV-2 (COVIS-19) 薬スクリーニング
COVID-19は、重症急性呼吸器症候群コロナウイルス2、SARS-CoV-2 による感染症です。初期の症状は比較的軽度である場合もありますが、ウィルスが健康な肺組織に損傷を与えて破壊するため、急性呼吸窮迫症候群(ARDS)に発展することもあります。Maestro システムでは、ウイルスによる細胞変性効果(CPE)を簡単に検出することが可能です。
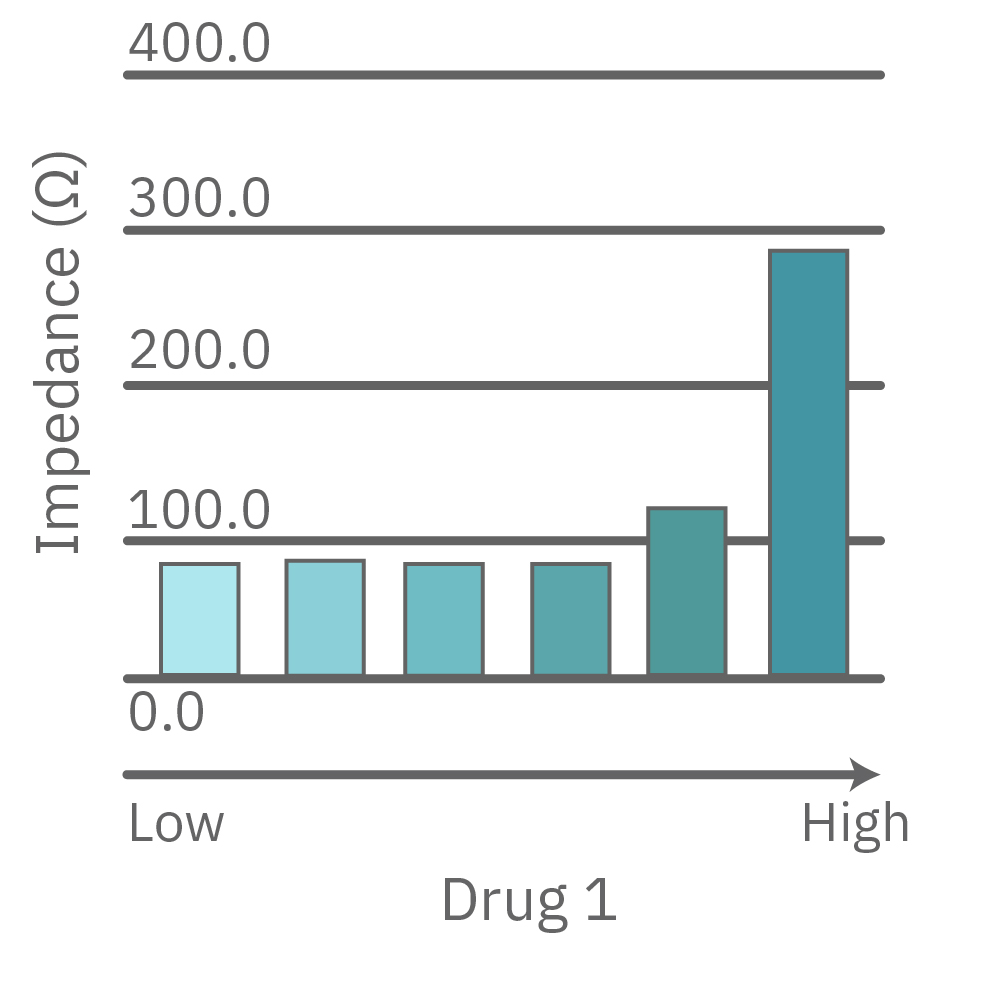
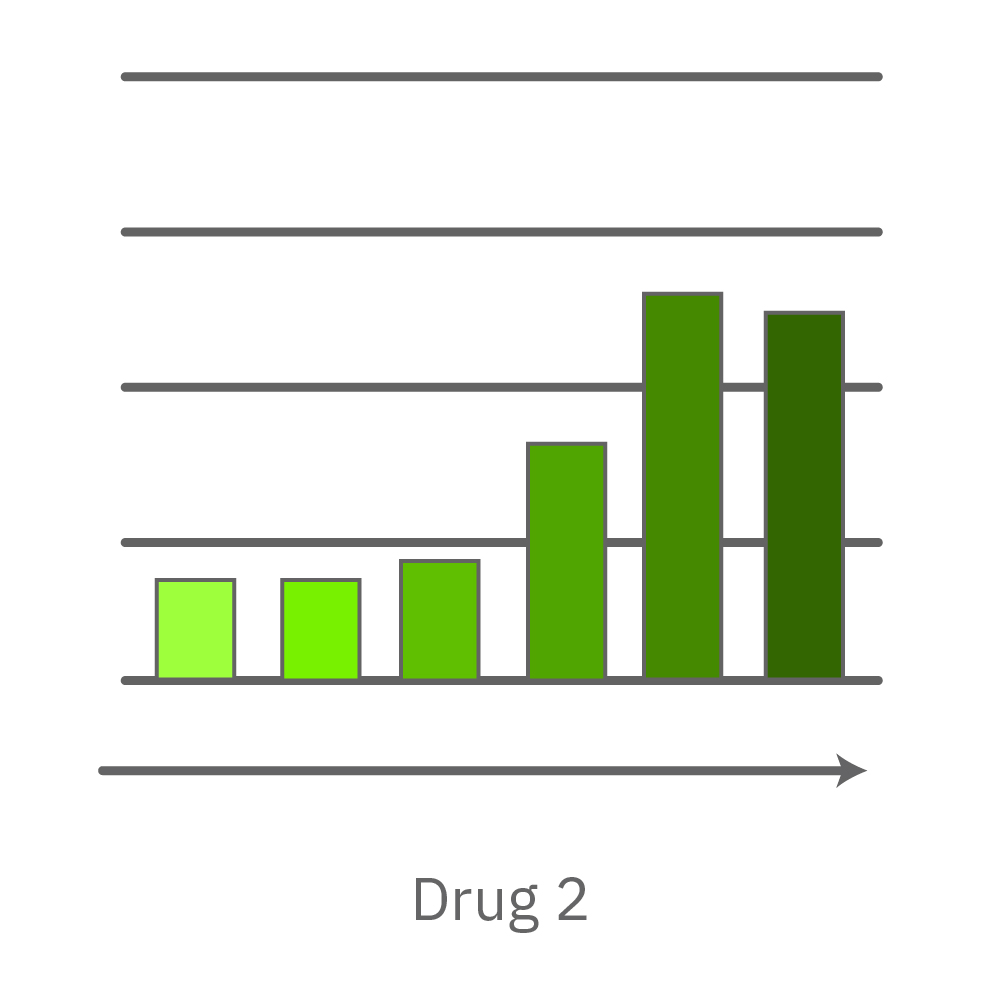
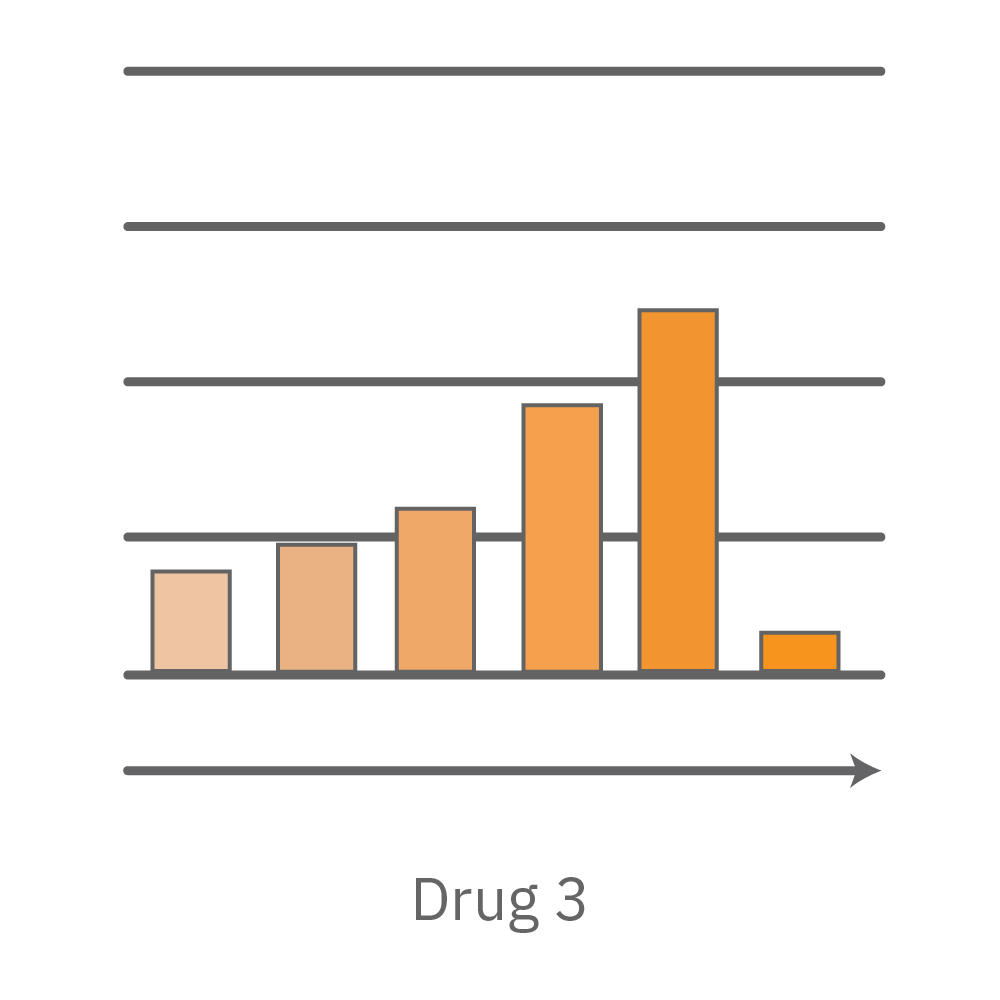
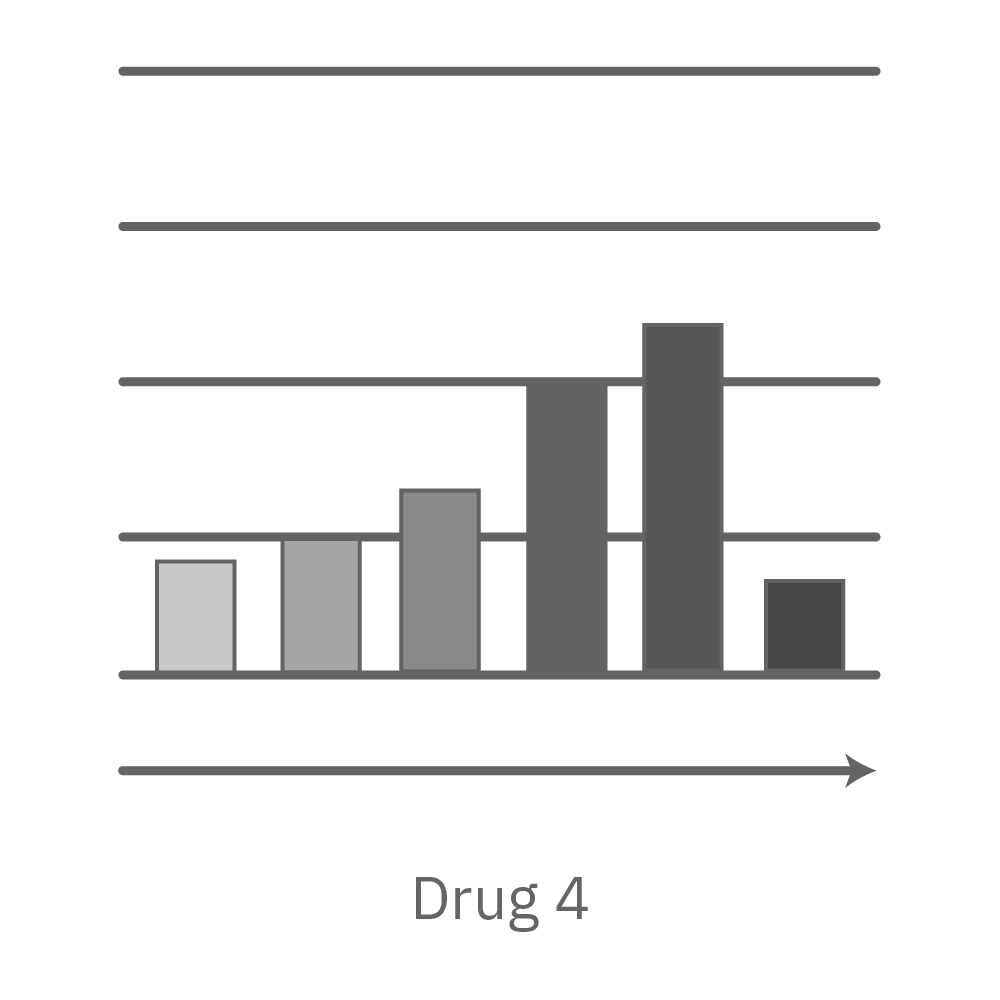
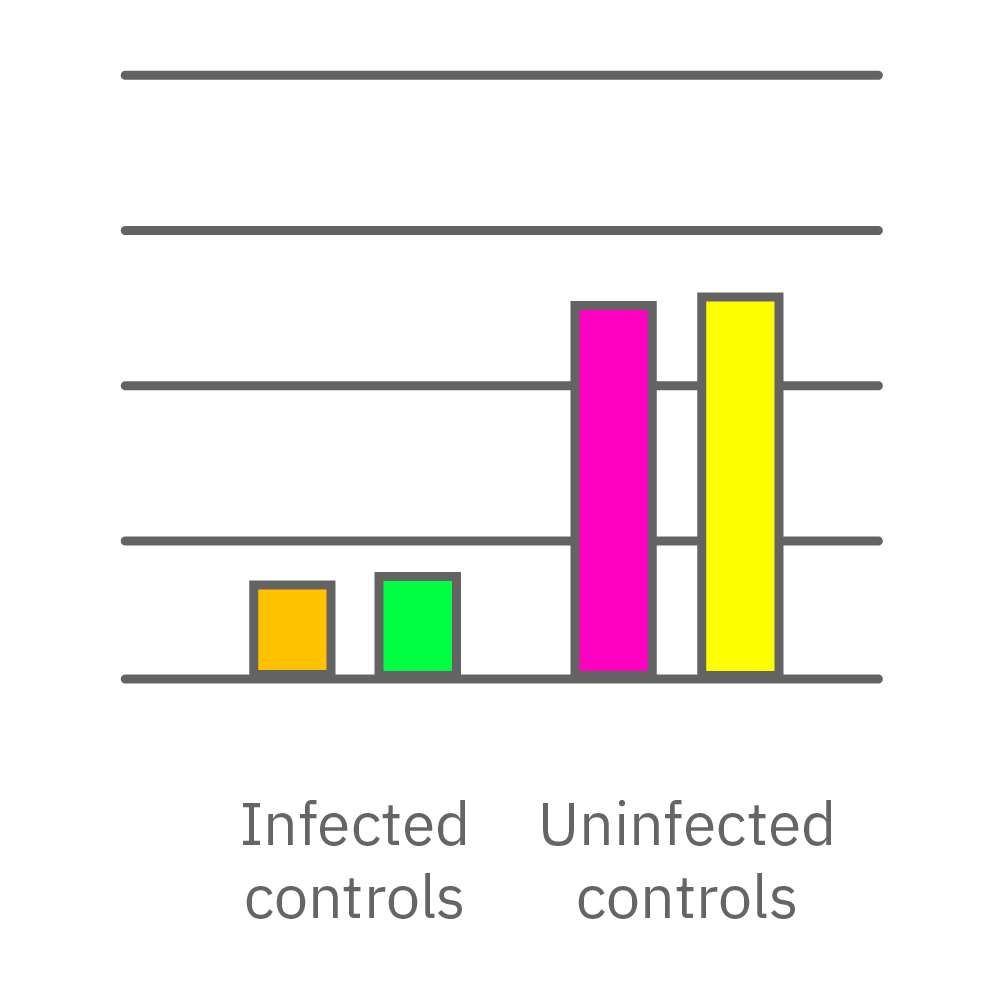
CytoView Z プレート上にVero E6 細胞を播種し、Maestro Zにてインピーダンスを測定した。播種から24時間後、SARS-CoV-2ウィルスと抗ウィルス化合物 (Drug 1, 2, 3, 4)を異なる濃度で添加し、継続してインピーダンスを測定した。いずれの薬剤においても、濃度依存的な細胞生存率(高濃度下においてインピーダンスが高い) が得られた。Drug3、4においては最高濃度で著しいインピーダンスの減少が得られ、強い細胞毒性が示唆された。最右表は、コントロールのインピーダンス値を表す。ウィルスのみ添加のVero E6細胞 (Infected controls) は低いインピーダンス (細胞死) を示し、ウィルス非添加の細胞 (Uninfected controls) は高いインピーダンス(細胞生存)を示した。
レムデシビルによる SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) 細胞死抑制効果の検証
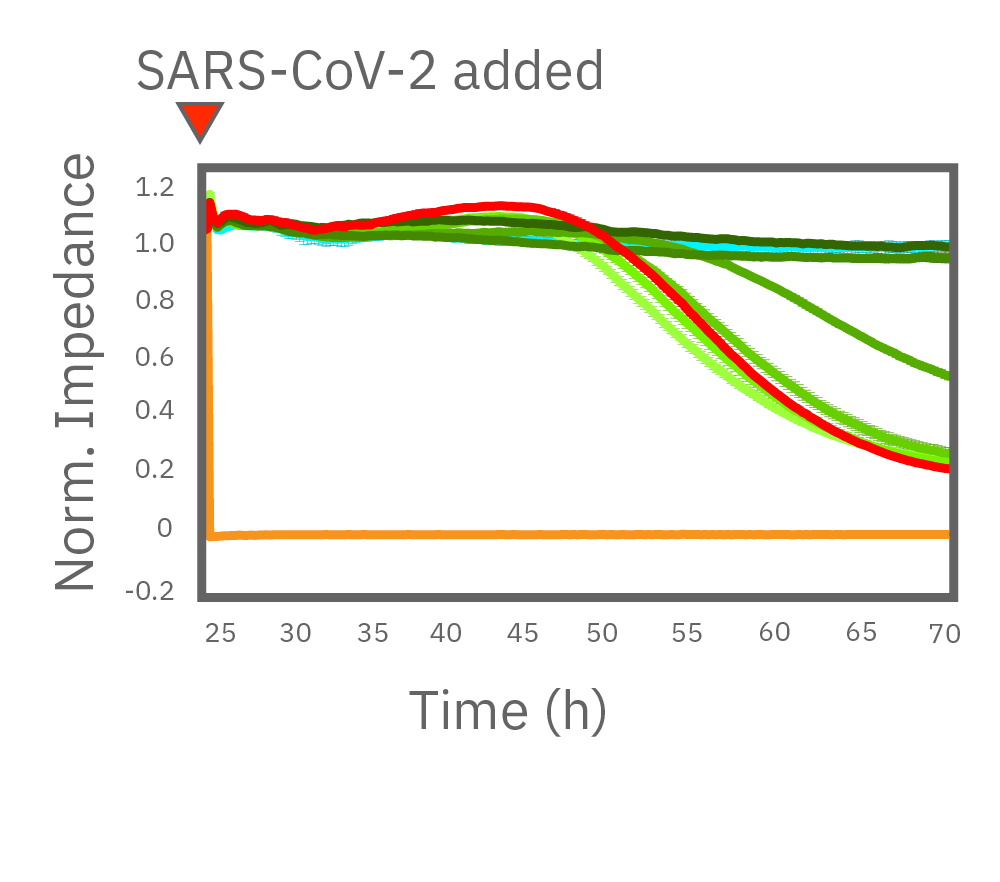
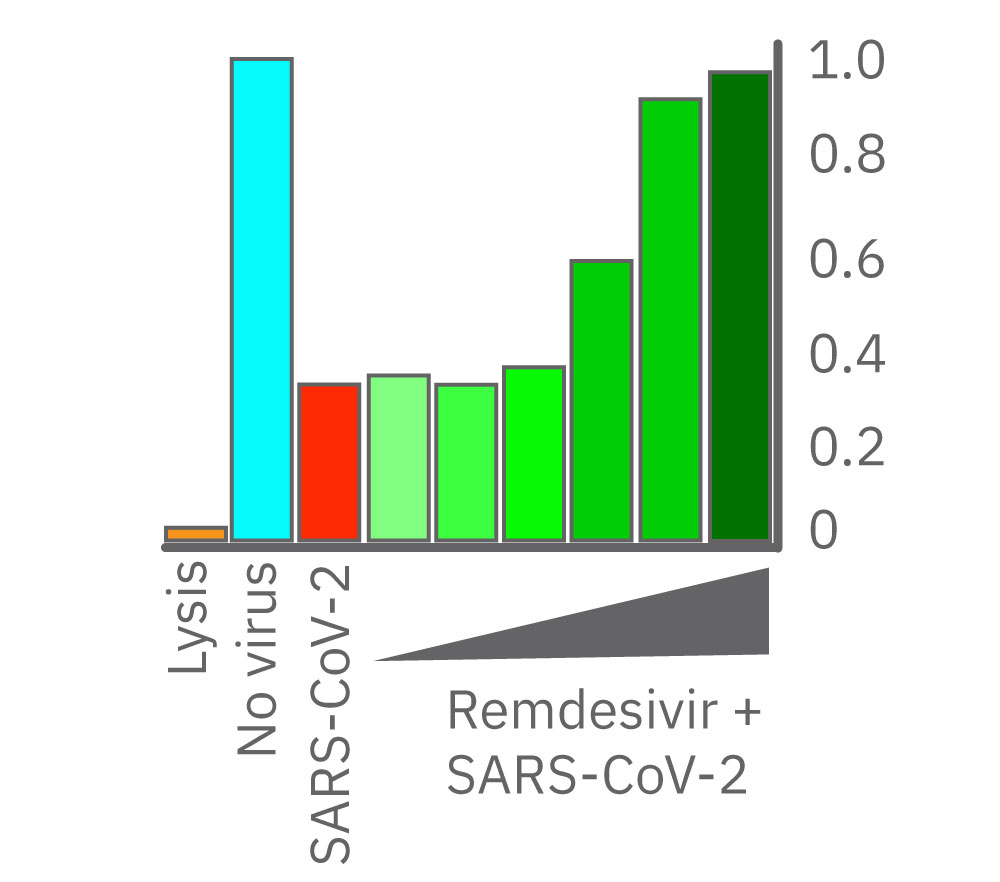
(左図)CytoView Zプレート上に Vero E6 細胞を播種しインピーダンスを測定した。24時間後、SARS-CoV-2と6濃度 (0.006, 0.038, 0.23, 1.38, 8.3, 50 μM) のレムデシビルを添加し、継続してインピーダンスを測定した。グラフはレムデシビル投与後からのインピーダンスの変化を示す。1.38 μM 以上の濃度で細胞死の抑制が得られた。
(右図) レムデシビル投与から48時間後のインピーダンスを示す。8.3 μM 及び50 μM 添加のVero E6細胞 (濃緑色) は非感染 (水色) と同等の細胞生存率を示した。一方、低濃度投与では顕著な変化が得られなかった。(データ提供: Drs Alex Jureka、Chris Basler, Georgia State University)
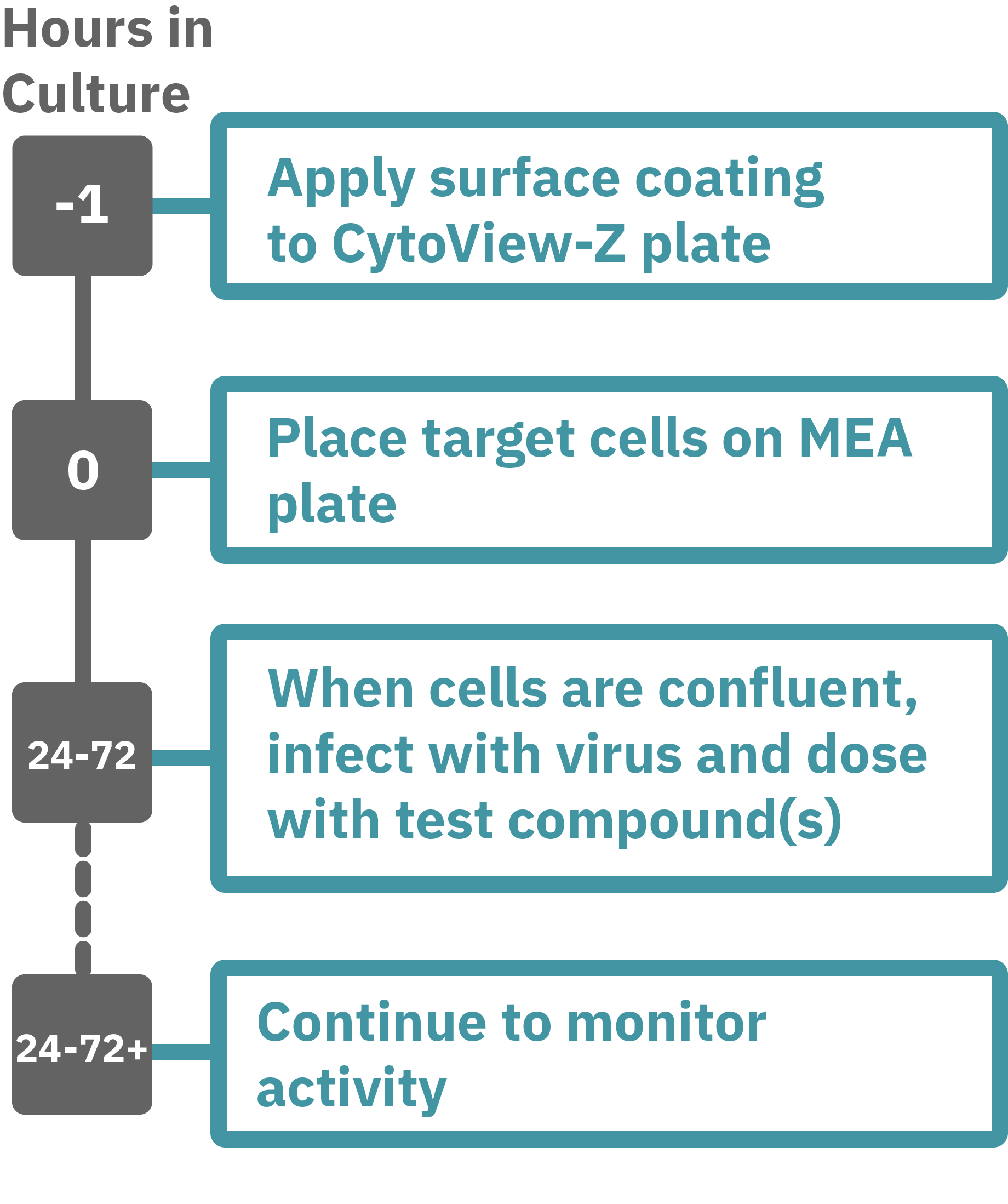
Maestroによる、インピーダンスアッセイはとても簡単です。事前コーティングされた CytoView-Z プレート上に細胞を播種します (Hour 0)。Maestroシステムにプレートを搭載すると同時に、温度・CO₂ 濃度制御とインピーダンス測定が開始されます。細胞の増殖・電極への接着に伴いインピーダンスが上昇します (Hour 24-72)。
細胞がプレート上でコンフルな状態になったら、ウィルス、抗ウィルス薬を添加し、ウィルスによる細胞変性効果 (CPE) と、その抑制をトラッキングします
細胞の変化はラベルフリーで測定され、リアルタイムにソフトウエア上に表示されます。測定終了後は付属のソフトで解析します。

Maestro Z/ ZHT, Pro/Edgeによる抗ウィルス薬評価:特徴
-
経時的観察 – 細胞の変化をリアルタイムで連続して測定します。ウィルスによる細胞変性効果 (CPEs) をリアルタイムでトラッキングすることが可能です。
-
ラベルフリー – 平面電極にてインピーダンスを測定し、染色・試薬なども不要です。ラベルフリー測定で数日間に渡る測定・観察が可能です。
-
インキュベータ不要 – Maestroには温度・CO2濃度コントローラが内蔵されています。インキュベータ等の周辺装置は不要。安定した環境下で数日間に渡る連続測定が可能です。
-
細胞可視 – CytoView-Z 96 well プレート底面中央部は透明になっています。必要に応じて、細胞の観察が可能です。
-
培養から測定まで同一プレート使用 – アッセイの全行程を同一プレートで行います。他のハイスループット・プラットフォーム(例:フローサイトメータ)のような容器の入れ替えなどは不要。細胞への負担を最小限に抑えることができます。
-
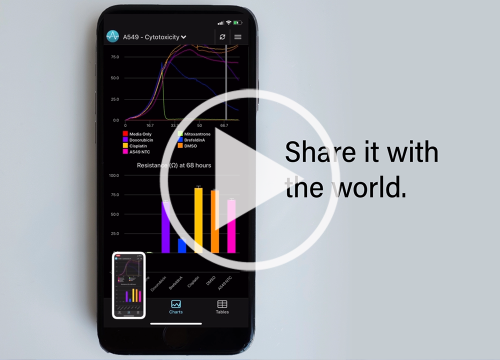
スマートフォン・アプリ – 専用のスマートフォンアプリに対応しています。数日間に渡る細胞変性効果 (CPEs) の様子を、実験室の外からでも、リアルタイムに観察して頂けます。
-
簡単 – セミ・オートメーションシステムです。ハードウエアの操作はボタン1つ。専用のソフトは、インピーダンスの変化をリアルタイムで表示します。解析結果のエクスポートも容易です。

Impedance
Show Full DetailsImpedance: For real-time cell analysis
Impedance-based cell analysis is a well-established technique for monitoring the presence, morphology, and behavior of cells in culture. Impedance describes the obstruction to alternating current flow. To measure impedance, small electrical currents are delivered to electrodes embedded in a cell culture substrate. The opposition to current flow from one electrode to another defines the impedance of the cell-electrode interface. When cells are present and attached to the substrate, they block these electrical currents and are detected as an increase in impedance.
Impedance is sensitive to many aspects of cell behavior: attachment, spreading, shape, cell-cell connections (e.g. tight junctions), and death. Even small transient changes, such as swelling or signaling, are detectable by impedance. Because impedance is noninvasive and label free, the dynamics of these changes can be monitored in real time over minutes, hours, or even days without disturbing the biology.
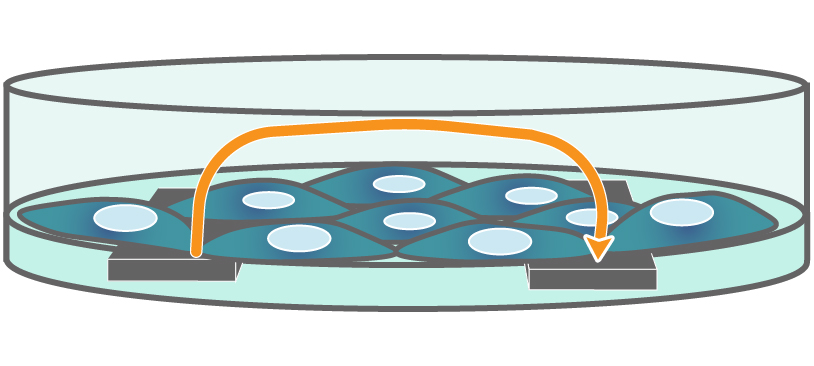
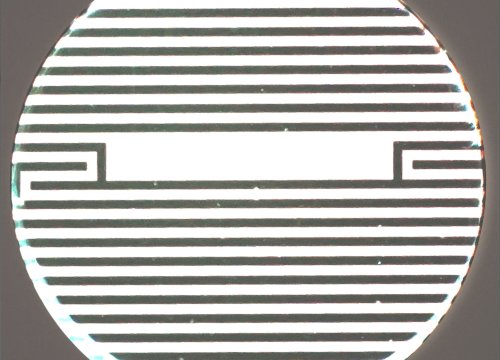
Interdigitated electrodes embedded in the cell culture substrate at the bottom of each well detect small changes in the impedance of current flow caused by cell presence, attachment, and behavior.
In the example below, the electrodes are initially uncovered before cells are added. The electrical current passes easily and the impedance is low. When cells begin to attach and cover the electrodes, less electrical current passes and the impedance is high. After dosing with a cytotoxic agent, cells die or detach, and the impedance decreases back towards baseline.
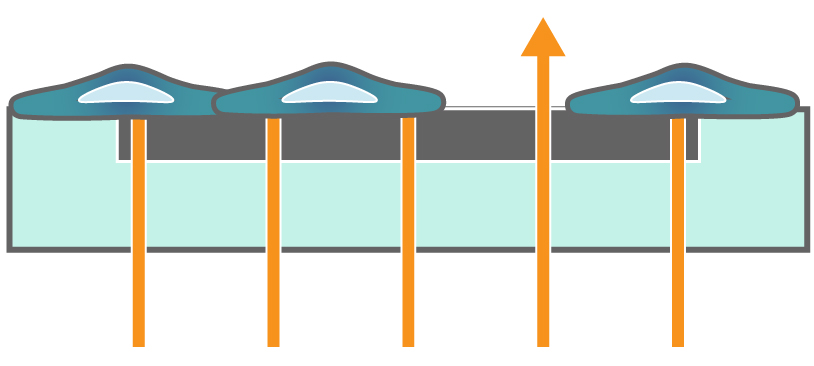
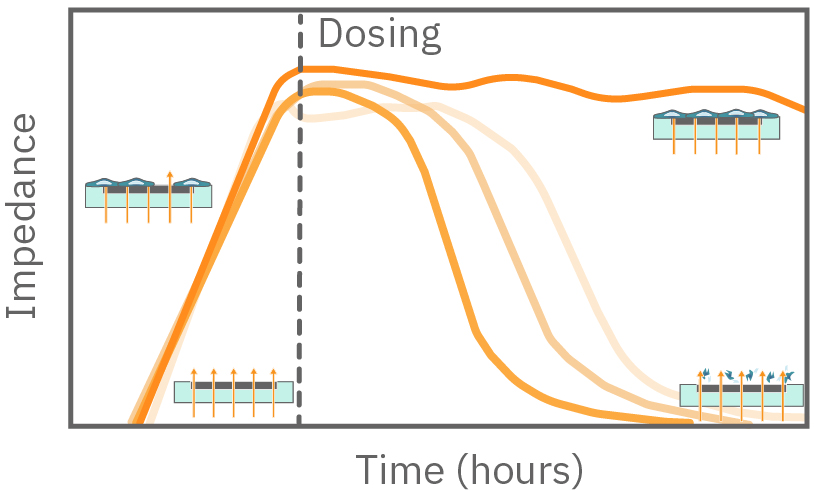
Impedance measures how much electrical signal (orange arrows) is blocked by the cell-electrode interface. Impedance increases as cells cover the electrode and decreases back to baseline due to cell death.
Continuous cell monitoring
Many cell-based assays are endpoint assays, limited to a single snapshot in time. Repeating these assays at multiple time points can be labor intensive, time consuming, and costly. Key time points can be easily missed. Impedance-based cell analysis is nondestructive and label free, meaning that cellular dynamics can be monitored continuously.
The impedance assay can be used to characterize dynamic cell profiles, revealing how cells grow, attach, and interact over time. Each cell type exhibits a different cell profile, or “fingerprint”, of dynamic cell behavior. These profiles are sensitive to cell type, density, purity, and environmental factors. In this example, the Maestro Z impedance assay readily distinguished cell profiles across different cell densities and cell types.
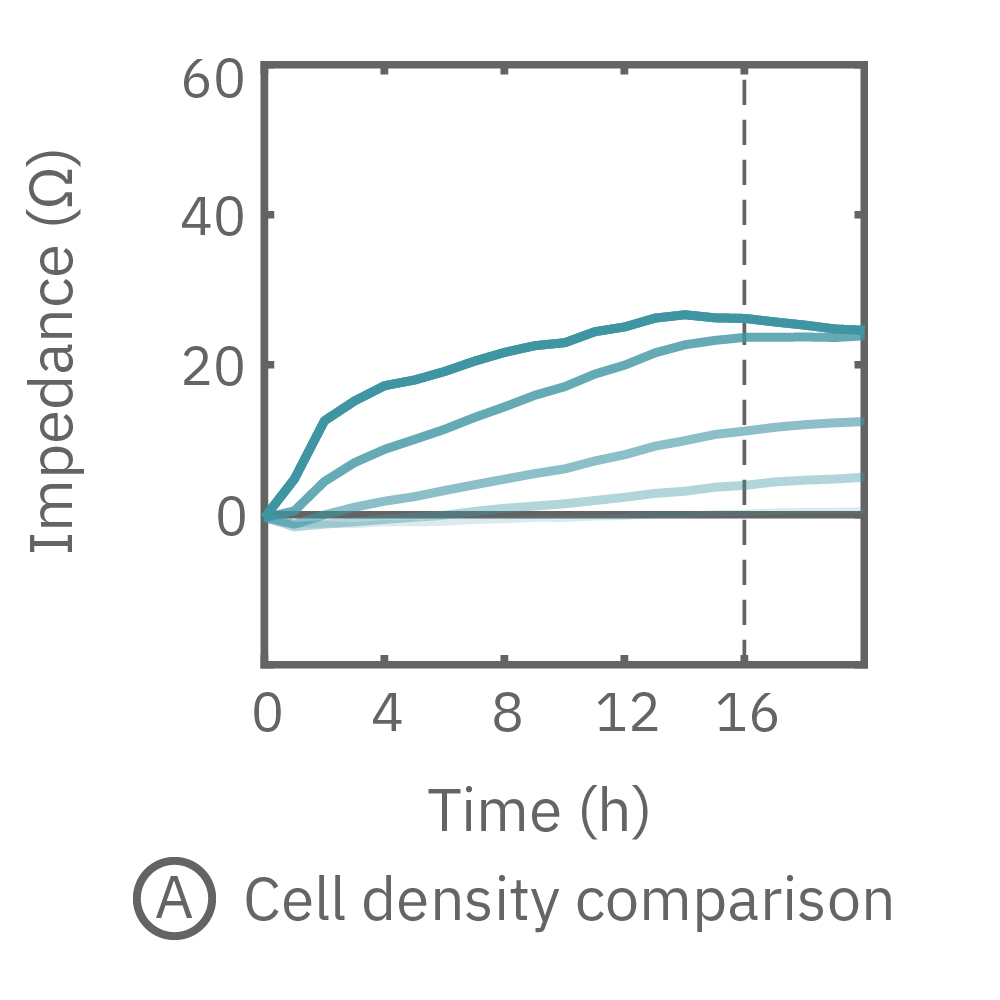
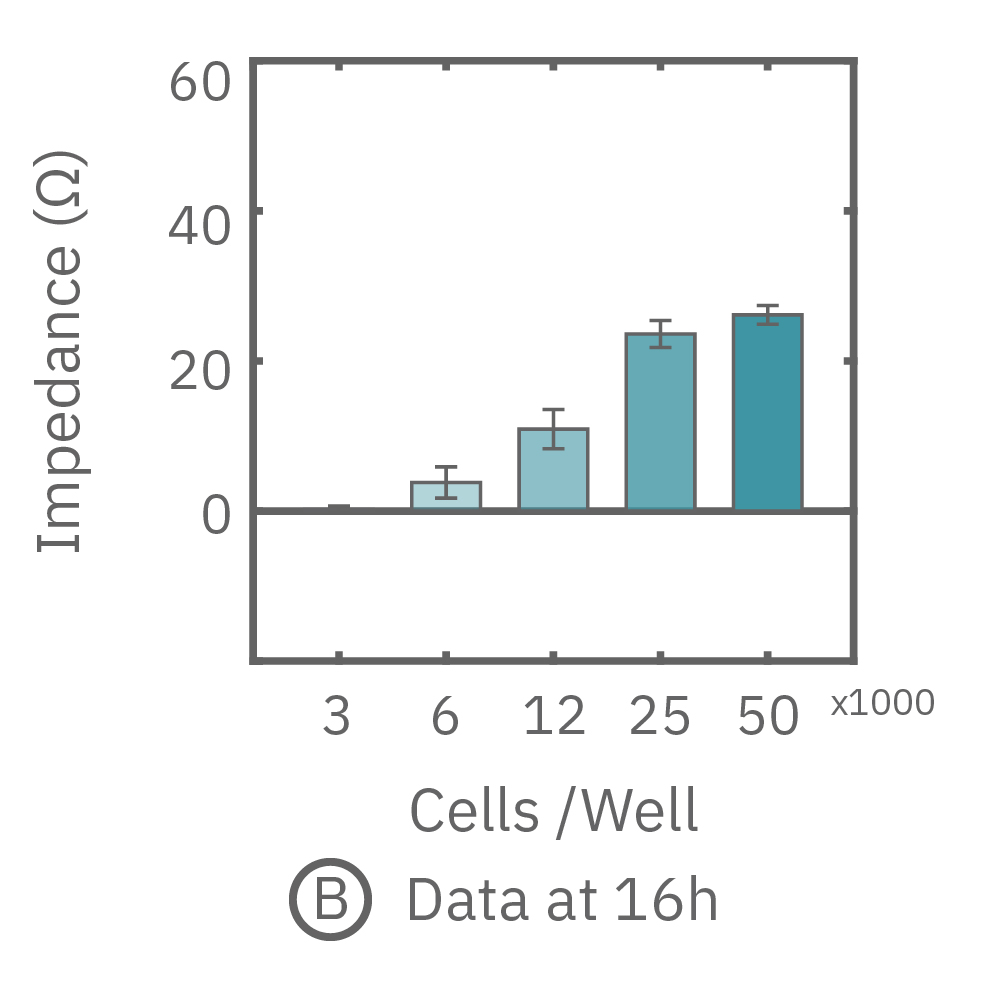
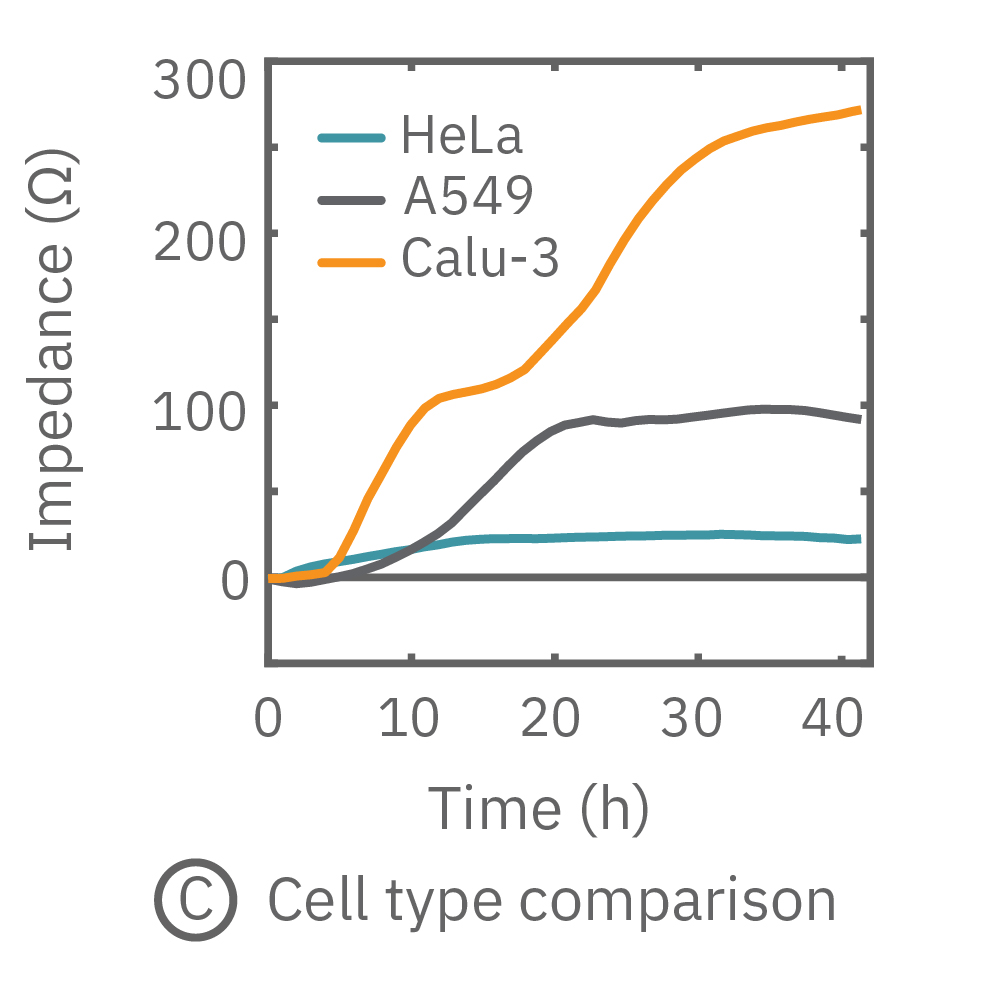
(A, B) HeLa cells were seeded on a CytoView-Z plate at varying densities and the impedance was continuously monitored by the Maestro Z. Impedance scaled proportionally with cell density and readily distinguished different densities of the same cell type. (C) Maestro monitored the growth of three cell types, HeLa, A549, and Calu-3, and readily distinguishes their distinct cell profiles over time.
The Maestro Z impedance assay can also be used to capture the kinetics of cell responses to drugs or immune cell therapies. The kinetics, which cannot be captured by endpoint assays, often provide key insights into the efficacy of novel therapies. In the example below, the Maestro Z impedance assay was used to quantify the kinetics of cytotoxicity of chemotherapy agents.
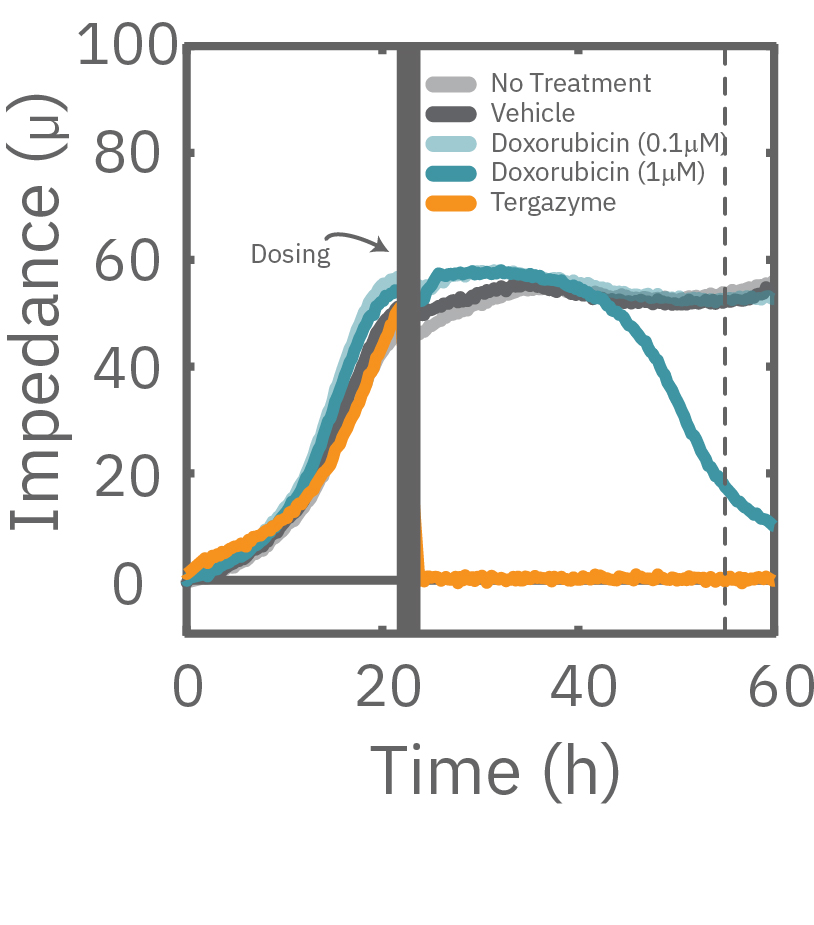
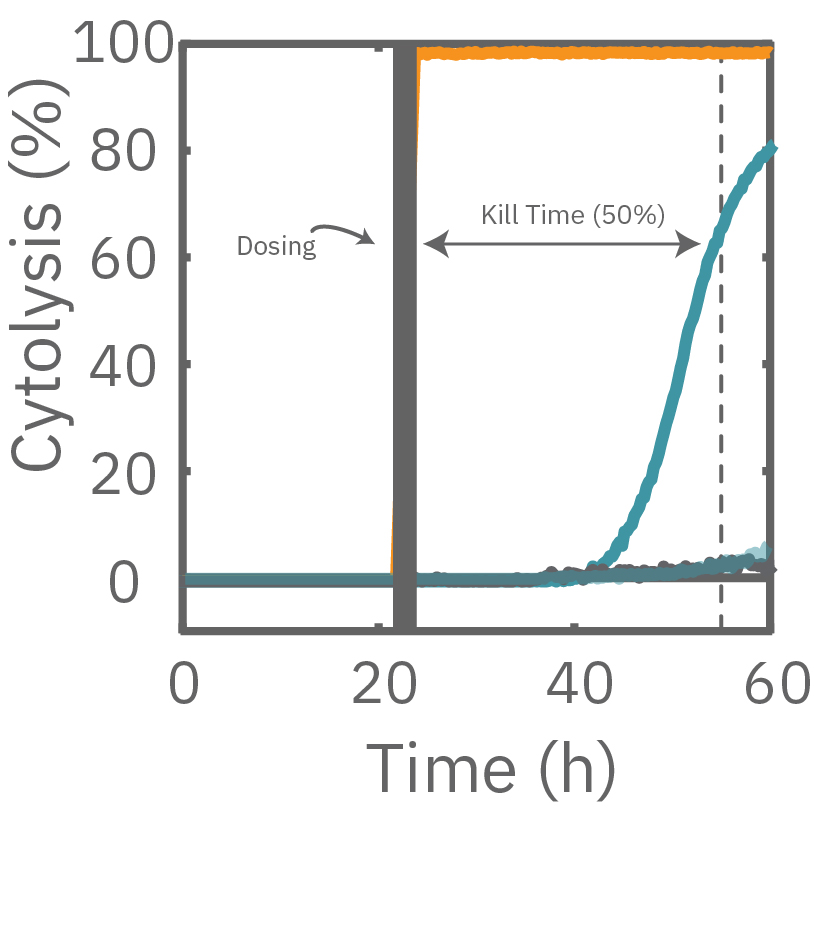
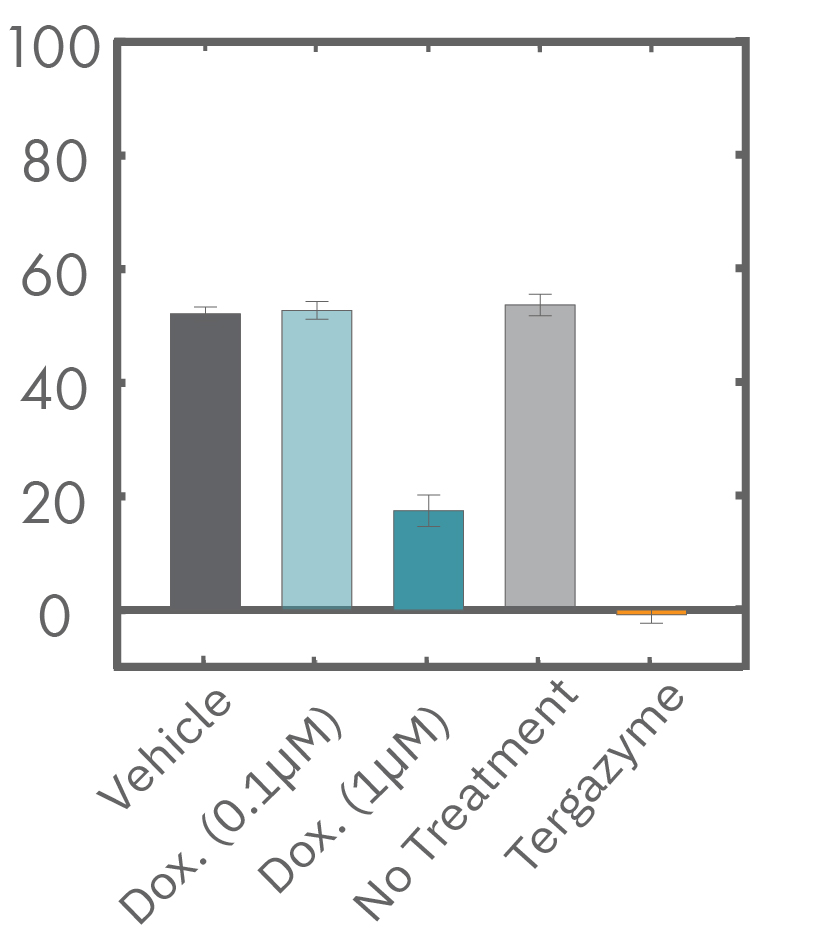
A549 cells were dosed with dox, vehicle (DMSO), or tergazyme. Wells dosed with tergazyme showed an immediate decrease in impedance, reflecting complete cell death. Higher doses of dox resulted in a slower decrease in impedance and cell death. Cells dosed with 1 μM dox reached 50% cytolysis at 31 hrs.
Different frequencies reveal cell properties
Impedance varies with frequency, such that different frequencies reveal different aspects of cell biology. The small currents used to measure impedance will always take the path of least resistance. At low frequencies, such as 1 kHz, the impedance of the cell membrane is relatively high, forcing the current to flow under and between the cells. Low frequencies provide details about barrier integrity, the presence of gap junctions, and transepithelial or transendothelial resistance (TEER).
At high frequencies, such as 41.5 kHz, the impedance (and capacitive reactance) of the cell membrane is relatively low. Thus, most of the current couples capacitively through the cell membranes, providing information about the cell layer such as confluency and coverage.
In other words, low frequencies are sensitive to “what” cells are there, whereas high frequencies are sensitive to “how many” cells are there. The Maestro Z impedance assay uses multiple frequencies to provide the most information about the cells, simultaneously, continuously, and in real time.
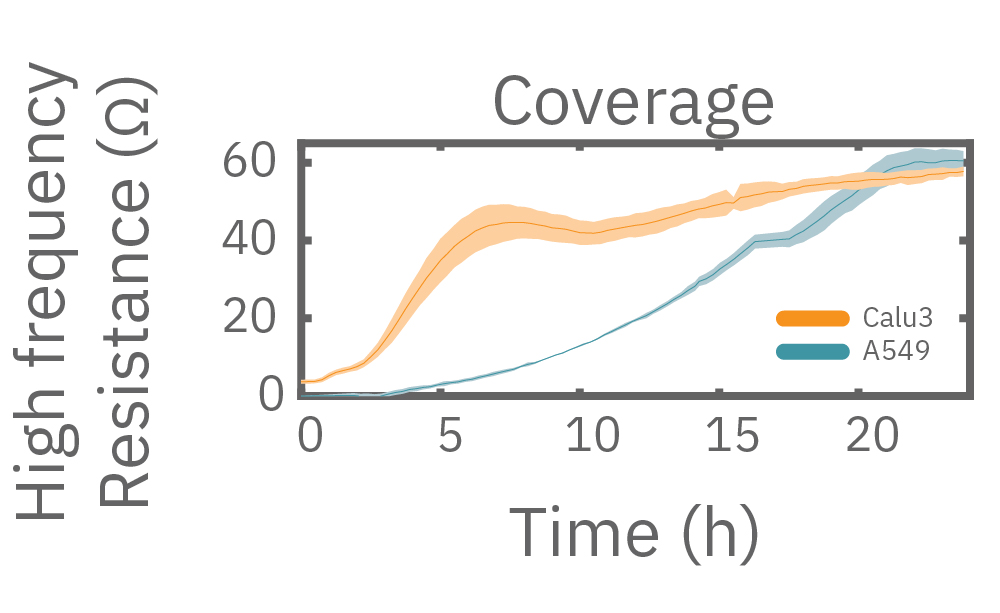
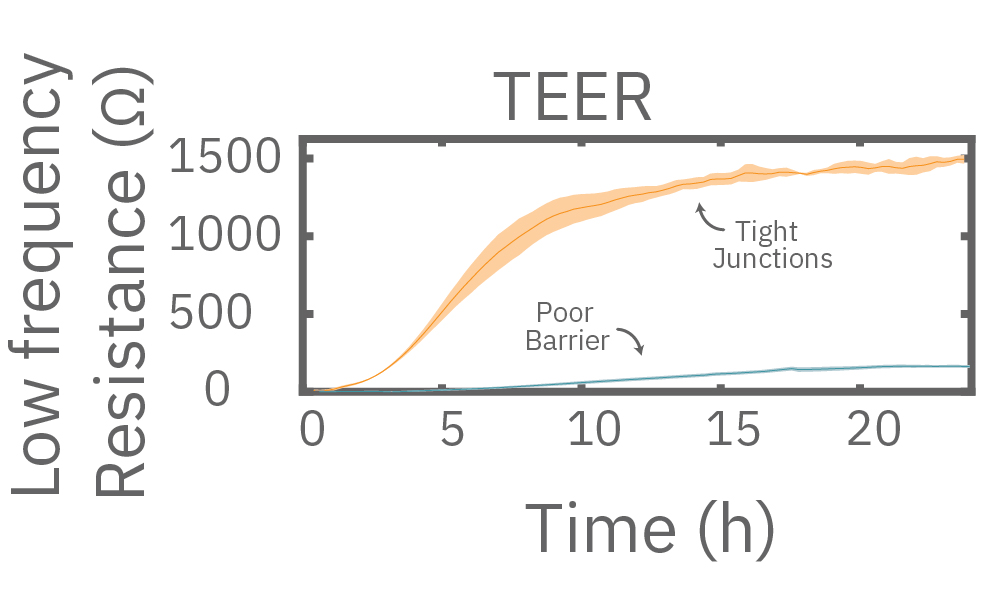
Multiple frequencies were used to simultaneously and continuously monitor the coverage and barrier function (TEER) of Calu-3 and A549 cells. Coverage, measured as resistance at 41.5 kHz, increases over time for both cell types. TEER, measured at 1 kHz, reveals that only Calu-3 cells form a strong barrier, as they express tight junctions to block flow between neighboring cells.